An array is a collection of similar type of elements which has contiguous memory location.
Java array is an object which contains elements of a similar data type. The elements of an array are stored in a contiguous memory location. It is a data structure where similar elements are stored.
Arrays in Java work differently than they do in C/C++. Following are some important points about Java arrays.
- In Java all arrays are dynamically allocated.
- Since arrays are objects in Java, we can find their length using the object property length. This is different from C/C++ where we find length using sizeof .
- A Java array variable can also be declared like other variables with [] after the data type.
- The variables in the array are ordered and each have an index beginning from 0.
- Java array can be also be used as a static field, a local variable or a method parameter.
- The size of an array must be specified by an int or short value and not long.
- The direct superclass of an array type is Object.
- Every array type implements the interfaces Cloneable and java.io.Serializable.
Types of Array in java
There are two types of array.
- Single Dimensional Array
- Multidimensional Array
One-Dimensional Arrays :
The general form of a one-dimensional array declaration is
type var-name[];
OR
type[] var-name;
An array declaration has two components: the type and the name. type declares the element type of the array. The element type determines the data type of each element that comprises the array.
Instantiating an Array in Java
When an array is declared, only a reference of array is created. To actually create or give memory to array, an array is created like :
var-name = new type [size];
Here, type specifies the type of data being allocated, size specifies the number of elements in the array,
and var-name is the name of array variable that is linked to the array.
Example:
int intArray[]; //declaring array
intArray = new int[20]; // allocating memory to array
OR
int[] intArray = new int[20]; // combining both statements in one
Accessing Java Array Elements using for Loop
Each element in the array is accessed using its index. The index begins with 0 and ends at (total array size)-1. All the elements of array can be accessed using for Loop.
// accessing the elements of the specified array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
System.out.println("Element at index " + i + " : "+ arr[i]);
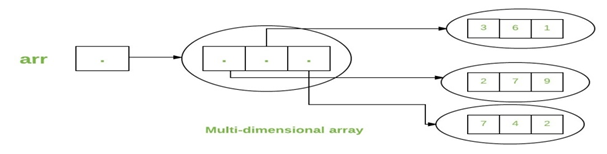
Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays with each element of the array holding the reference of other array. These are also known as Jagged Arrays.
A multidimensional array is created by appending one set of square brackets ([]) per dimension.
int[][] intArray = new int[10][20]; //a 2D array or matrix
int[][][] intArray = new int[10][20][10]; //a 3D array
for example an array
int arr[][] = { {2,7,9},{3,6,1},{7,4,2} };
is represented like

0 comments:
Post a Comment