An efficient solution to use a single array to store more than one queue is called multiqueue.
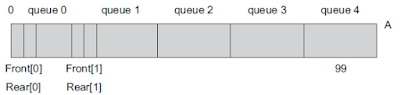
When more than two queues (say n) are to be represented sequentially, divide the available memory A[size] into n segments and allocate these segments to n queues, one to each.
For each queue i, Front[i] and Rear[i] are used. The condition Front[i] = Rear[i] is used if and only if the ith queue is empty, and the condition Rear[i] = Front[i] is used if and only if the ith queue is full.
If five queues are required, and array of 100 size is available then divide the array A[100] into equal parts of 20 and initialize front and rear for each queue, that is, Front[0] = Rear[0] = 0 and Front[1] = Rear[1] =
20, and so on for other queues.

0 comments:
Post a Comment